Understanding Venous Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
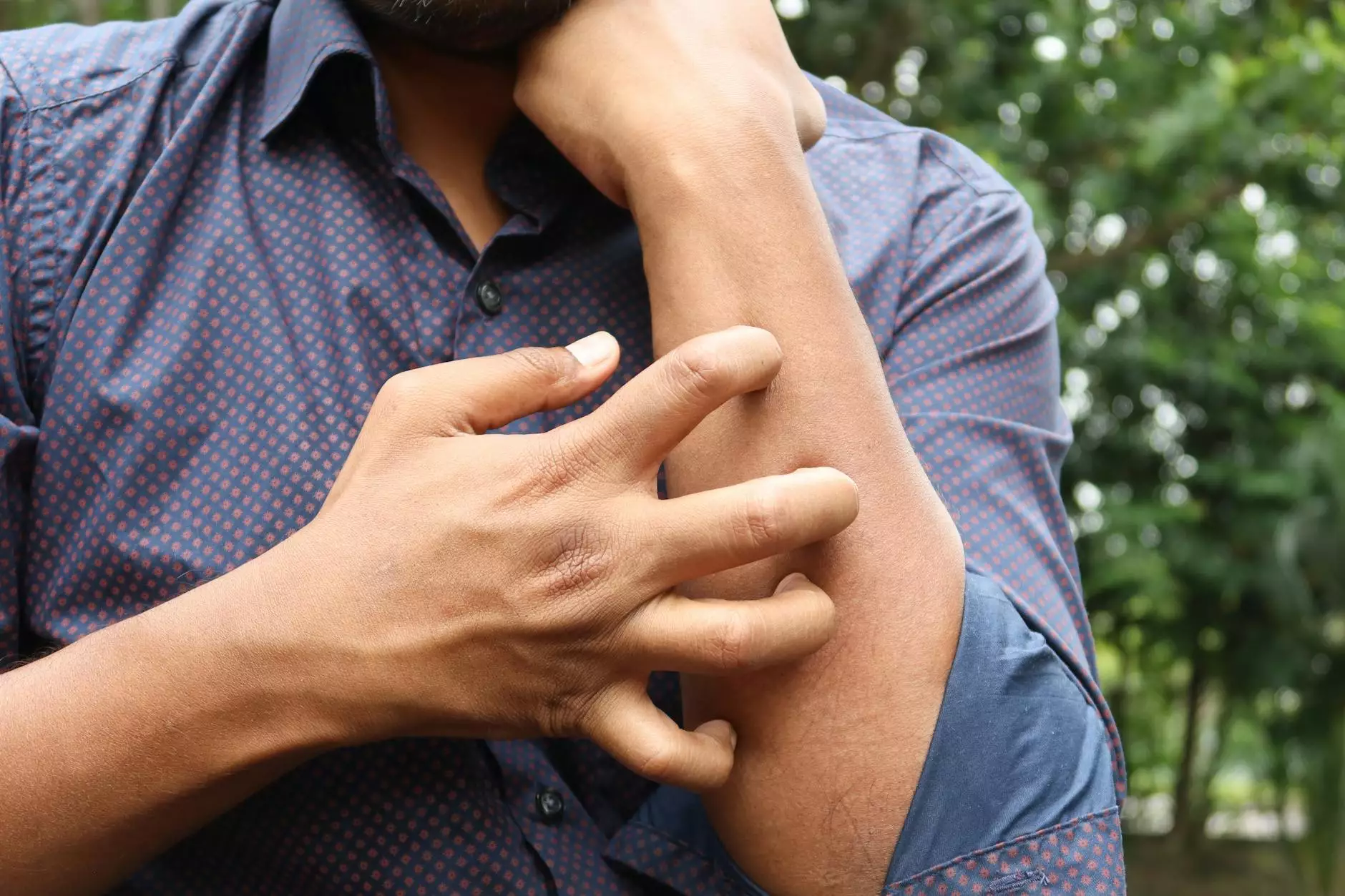

Venous dermatitis is a condition affecting the skin, often leading to discomfort and unsightly appearances. This article provides a detailed insight into this medical condition, exploring its etiology, manifestations, diagnostic approaches, and the myriad of treatment options available.
What is Venous Dermatitis?
Venous dermatitis, also known as stasis dermatitis, is a skin inflammation that typically occurs in individuals with chronic venous insufficiency. When the veins in the legs are unable to effectively return blood to the heart, blood can pool in the lower extremities. This pooling can lead to increased pressure, resulting in damage to the skin and surrounding tissues.
Causes of Venous Dermatitis
The underlying cause of venous dermatitis is primarily related to venous insufficiency. Here are some of the most common factors that contribute to this condition:
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency: The majority of patients with venous dermatitis have a history of chronic venous insufficient, where the arteries struggle to push blood back to the heart.
- Age: As people age, the risk of developing issues with their veins increases, contributing to potential instances of venous dermatitis.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can put additional pressure on the veins, worsening venous return and exacerbating symptoms.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Occupations that require long periods of standing or sitting can impact blood flow in the lower extremities.
- Previous Blood Clots: A history of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can severely impact venous health and lead to dermatitis.
Symptoms of Venous Dermatitis
Symptoms of venous dermatitis can vary from one individual to another but typically include:
- Itching: One of the earliest signs, often leading to further irritation and potential skin damage.
- Redness: Inflamed patches can appear as red, warm areas on the skin.
- Flaking or Peeling Skin: The affected area may also exhibit dryness, leading to flaky or peeling skin.
- Swelling: Lower leg swelling may occur due to fluid accumulation.
- Crusting or Oozing: In more severe cases, the dermatitis can lead to crusty lesions that might ooze fluid.
Diagnosis of Venous Dermatitis
Diagnosing venous dermatitis typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Healthcare providers may also utilize the following diagnostic tools:
- Ultrasound: This imaging technique helps assess venous function and detect any blockages in the veins.
- Venography: A special X-ray that uses contrast dye to visualize veins can occasionally be used.
- Clinical Evaluation: Dermatologists will examine the symptoms and determine any interacting dermatological conditions.
Treatment Options for Venous Dermatitis
Treating venous dermatitis usually focuses on managing the symptoms as well as addressing the underlying venous insufficiency. Below are several effective treatment options:
1. Compression Therapy
Compression stockings are often the first line of treatment. They work by applying graduated pressure to the legs, promoting better blood circulation and reducing swelling.
2. Topical Treatments
Topical corticosteroids can be used to alleviate inflammation and itching. Additionally, moisturizers and barrier creams can help maintain skin integrity.
3. Medications
Oral medications such as antihistamines may be prescribed for itching, while diuretics can help manage swelling in some cases.
4. Lifestyle Changes
Implementing lifestyle changes is crucial. This includes:
- Weight Management: Reducing weight can significantly impact venous health.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activities promotes healthy circulation.
- Avoiding Prolonged Positions: Changing positions frequently can help blood return to the heart more effectively.
5. Surgical Options
In extreme cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical options may be considered, such as:
- Vein Stripping: Involves surgically removing veins that contribute to the problems.
- Laser Treatments: Non-invasive procedures to close defective veins.
Prevention of Venous Dermatitis
Preventing venous dermatitis often hinges on managing its risk factors. Some effective preventative measures include:
- Staying Active: Regular exercise enhances overall circulation.
- Using Compression Stockings: Wearing them during prolonged periods of standing or sitting can reduce the risk of venous issues.
- Elevation: Elevating the legs, especially while resting, can aid in venous return.
Conclusion
In conclusion, venous dermatitis is a significant condition that deserves attention. With appropriate strategies for diagnosis and treatment, individuals can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms related to venous dermatitis, consulting with a specialist such as those at Truffles Vein Specialists is crucial for tailored care and intervention.
Understanding and addressing venous health intricacies can prevent the advancement of skin conditions like venous dermatitis and lead to healthier lives.